Find out what your IPv4 and IPv6 addresses are, along with detailed geolocation insights, including the associated country, city, and ISP, below.
| IPv4 | 216.73.216.87 |
| IPv6 | Checking... |
| Country | United States |
| Region | Ohio |
| City | Columbus |
| ZIP | 43215 |
| ISP | Amazon.com |
| Org | Anthropic, PBC |
| ASN | AS16509 Amazon.com, Inc. |
| Timezone | America/New_York |
| User Agent | Mozilla/5.0 AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko; compatible; ClaudeBot/1.0; [email protected]) |
Disclaimer: Please note that the location marked on this map for the IP address is an approximation and may not accurately represent the actual physical location due to factors like IP address reallocation, proxy usage, and the geographic distribution methods used by internet service providers.
What is an IP address?
An IP address (Internet Protocol address) is a unique number which is assigned in every device in a network. It ensures that proper data routing is performed to assist you in identifying devices in the TCP/IP architecture. The IP addresses are the points of communication through which routers can forward these packets with the help of the routing tables and prefix matching. They usually operate in conjunction with subnet masks to partition networks, assist NAT in order to translate private addresses and employ DHCP to automatically assign these addresses. Each device that utilizes internet access, such as computers, smartphones or IoT devices, depends on these IP addresses. Logical addressing ensures that this information is consistent in data transportation and connectivity appears instantaneous in global networks.
Types of IP Addresses
There are an increasing number of internet-connected devices that exhausted all the available IPv4 addresses and pushed the development of more advanced protocols. This shift was necessary to support global connectivity, improved performance and long term scalability.
IPv4
It is the fourth version of the Internet Protocol that uses 32-bit addresses written in dotted-decimal format that support around 4.3 billion unique identifiers. IPv4 addresses use four 8-bit segments that range from 0 to 255. This fourth version IPv4 supports classful and classless addressing. It uses Classless Inter-Domain Routing(CIDR) to route the suggestions and the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) to map any IP addresses to MAC addresses. It includes a header checksum for error detection, fragmentation for handling large packets, and Time To Live (TTL) to prevent infinite loops. IPv4 is applicable in most of the networks but depends on Network Address Translation(NAT) to extend the limited address space. NAT maps private IP addresses to a public IP, which causes latency and affects peer-to-peer communication.
IPv6
IPv6 is version 6 of Internet Protocol. It was designed to replace IPv4 and solve its limitations. It uses a 128-bit address format written in hexadecimal and separated by colons like2001:4860:4860:0:0:0:0:8888. It supports around 340 undecillion unique addresses. This allows every device to have a globally unique IP. IPv6 removes the need for Network Address Translation (NAT) which makes the communication more faster and direct. It supports SLAAC for self-configuration and uses built-in IPSec for secure data transfer. It improves routing efficiency using simplified header structures and supports efficient multicast instead of broadcast. IPv6 is essential for future networks, IoT systems, and global connectivity.
Static and Dynamic IP Addresses
The way IP addresses are assigned affects network performance and scalability. IPs can be either static or dynamic depending on how they are configured. Let's understand in detail:
Static IP
A static IP address is a fixed and manually configured network identifier that does not change over time. Endpoint visibility is essential for servers, routers and devices that needs to be addressed constantly.
In predictable routing like DNS servers, email servers and remote access solutions use static IPs. They reduce routing table recalculation and maintain persistent network sessions. DHCP lease conflicts avoid static assignment to enable firewall rule hardening and support port forwarding configurations with reliability. For careful planning and documentation Static IPs require predictable routing, such as DNS servers, email servers, and remote access solutions. Later, it can result in inefficient use of IP space in environments with high device mobility or scaling demands.
Dynamic IP
A dynamic IP address is an IP address that is assigned to a device for a limited amount of time by a DHCP server. It is taken from a range of addresses and usually changes with every new session or by a specified lease time.
Dynamic IP configuration is done automatically and also lets you configure a network with less manual input. Dynamic is also the best option for the end-user devices like laptops, smartphones, etc. and other devices where a static means of identifying is not needed such as IoT devices. Having dynamic IPs allows for quick reuse of IP addresses across devices, reduction in human error when configuring devices manually with static IP addresses, and faster end-user onboarding within specific scopes or environments, especially with a cloud data center and public Wi-Fi networks. However, dynamic IPs are less than desirable for end-user devices when hosting services that require consistent and stable endpoints unless you have other tools like Dynamic DNS or DHCP reservation.
How to find my IP Address?
IP addresses can be found simply by searching “what is my IP” in any web browser. Sites like whatismyip.org or ipinfo.io will show you your current public IP right away in search engines and websites. In this way, the IP address that your Internet Service Provider (ISP) gives you and that you use to talk to others online. You can also retrieve your device’s private IP address, which is used only on your local network, by going to the network settings on your device.
How to find your IP on Windows?
Windows operating systems provide multiple built-in methods for IP address discovery through both graphical interfaces and command-line utilities. Let's understand each method below:
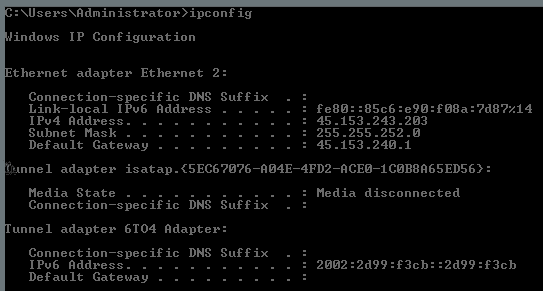
1. Command Prompt Method
- Press Windows key + R to open Run dialog
- Type “cmd” and press Enter to launch Command Prompt
- Execute “ipconfig” for basic IP address information
- Use “ipconfig /all” for detailed network configuration including DNS servers and subnet masks
- Locate your IP address under the active network adapter section
2. Windows Settings Approach
- Click Start menu and then Settings (gear icon)
- Go to Network & Internet settings
- Choose your active connection (Wi-Fi or Ethernet)
- Click on “Properties” or “Advanced options”
- See IP address details in the network details section
3. PowerShell Advanced Method
- Right-click the Start button and choose “Windows PowerShell”
- Run “Get-NetIPAddress” for detailed network enumeration
- Filter results with “Get-NetIPAddress -AddressFamily IPv4” for IPv4 addresses alone
How to find your IP on macOS?
macOS systems integrate IP address discovery through both Terminal commands and System Preferences interfaces, providing flexible access methods for technical users and general consumers seeking network configuration details.
1. System Preferences Method
- Go to System Preferences > Network
- Select your network connection to view the IP
2. Terminal Method
- Open Terminal application (Applications > Utilities > Terminal)
- Execute “ifconfig” command for complete network interface information
- Use “ifconfig en0” to display specific Wi-Fi adapter details
- Run “ipconfig getifaddr en0” for direct IP address output
- Locate inet address entries for your IP configuration
3. Alternative Terminal Commands
- Use “networksetup -getinfo Wi-Fi” for detailed wireless configuration
- Execute “hostname -I” for quick IP address identification
- Run “ifconfig | grep inet” to filter IP address entries specifically
Regardless of whether your interest is in discovering your public address, or if you have a need to access your device’s local network address for some troubleshooting, these methods enable you to rapidly and easily discover your IP.
What is IP Address Geolocation?
IP Address Geolocation is the process of finding the approximate physical location of a device based on its IP address is called IP Address Geolocation. It identifies your details like city, region, country and sometimes even coordinates using ISP routing data and IP mapping databases. This technology supports content localization, targeted ads and regulatory compliance. Geolocation services integrate with web apps and security systems to enhance user experience while it prevents misuse. It is generally accurate at the city level for residential users but the accuracy may vary due to VPNs, proxies and mobile networks. Websites like WhatIsMyIP allow users to check the approximate location of any IP address.
Can I hide my IP?
Yes, you can hide your IP address using VPNs, proxy servers and the Tor browser. A VPN encrypts your connection and it routes toward another server so websites see the IP of the the VPN and not yours. Proxies forward your traffic and can mask your identity. The Tor browser provides extra layers of privacy as it will bounce your data through multiple nodes. Using public Wi-Fi may temporarily change what your visible IP, however, it can also have security risks. While these methods will help protect you from online activity, help maintain your privacy, and help you bypass restrictions that may be based upon your location.